22.02.14 - Req. Modelling
Work models help you take the next leab in understandning from knowing the work of individual stakeholders to understandning the fundamental structure of work for a whole stakeholder population
What are requirement models for?
Requirements Models
- Synthesising all the requirements you collected into key requiremnts
- You start making diagrams that represent how requirements relate
- Then you have a comprehensive set of intergrated requirements
- Representaiton of how something works
- Different representaiton convey different useful benefits
- Models are selective representations to portray an important aspect
Most important thing
- What do you want to show
- Which diagram or model is best for this
Context Diagrams
Identify number of systems will have to interact with Want to show how all these systems inter-relate
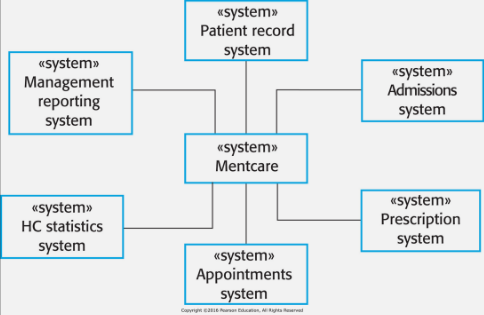
Shows related systems
Often part of Non-Functional requirements
Defines the boundaries of the system
Represent key systems that need to be deployed
And the relationship to the other systems
Task Analysis
- For identifying sub tasks
- Still not good for process, nor decision points
UML Diagrams
- Used to be 3 popular approaches to producing models, 1990 got unified then got UML 2 with 13 different diagrams
5 Key diagram tyoes
- Behaviour Diagrams
- Use case diagram
- Activity Diagrams
- Sequence Diagrams
- Structure Diagrams
- Class Diagrams
- State Diagrams
Activity Diagrams
- Used to elaborate workflows for key activities
- Explains the process, decision points, wait points and parallel points
- Usually to define one Use Case in more detail
- May tie together several use cases for one bigger process
Sequence Diagrams
- Good for sharing information between people and systems
- Series of messages between key components
- Can be used to specify function calls in java
Class Diagrams
- Specify the classes in oops code
- A lot like a Entity relationship diagram, done well, more like a specification
State Diagrams
- All the states that something can be in
- And what actions can change it
Scenarios
- Must define a setting or context
- Must define one or more actors or users
- Must define goals or objectives
- Must describe a plot
- Describes how a user, in a context, achieves a goal
- Written text descriptions